Bitcoin, Blockchain and Distributed Ledgers - Look Before You Leap
Organizing the Landscape to Identify Potential Markets
A Viewpoint from 10,000 Feet
I am attempting to tell a story of what the “blockchain” innovation is and where it fits into a technology landscape. In addition, I try to describe why this innovation is important and how it creates value.
In order to put this all together, I build a theoretical model from within an economic context — transaction costs and agency costs. This model gives the reader, particularly those not familiar with economic theory, another perspective from which to understand and think more prudently about applying this innovation to the specific business challenge they are trying to solve.
The full article Look Before You Leap is available on my Google drive. It is roughly 4100 words and should be about a 20–25 minute read. Among other things, the article includes links to blog posts with specific tools for determining if you should use blockchain technology.
Some Highlights — 3 Take Aways and the Technology Tree Diagram
1)The story of blockchain is a tale about databases. The main character is a new type of database software running on a distributed computer network.
- The distributed network is a peer-to-peer network.
- The software employs consensus algorithms that enable the computers to create trust amongst themselves and thus become the trusted validation system — no need for a human based agency system to do this function any longer.
- Blockchain is located on the Database software branch of my Technology Tree (see below.) It is a grand child of Distributed Ledgers.
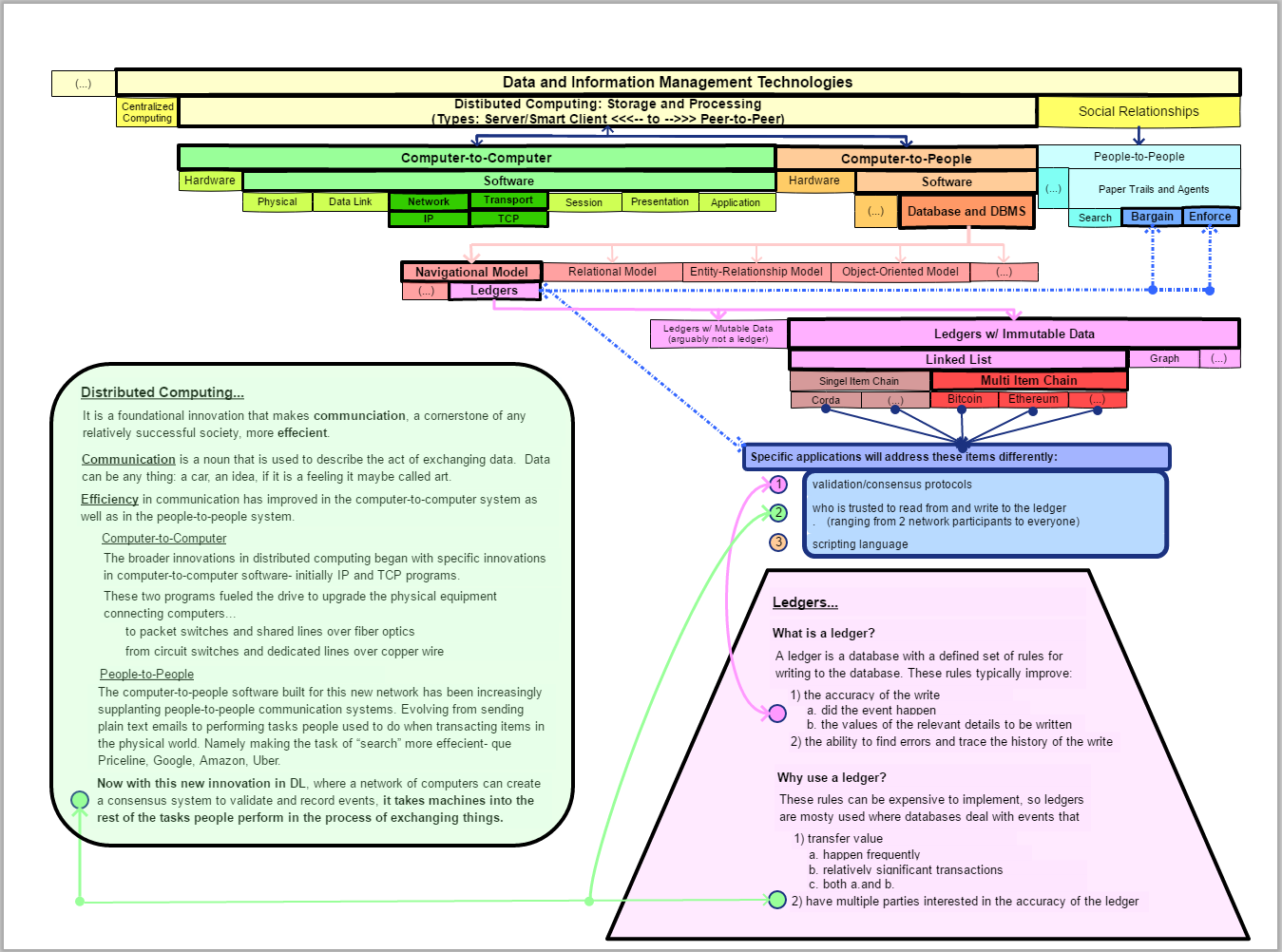
2)The new distributed database software is a continuation of a software wave that began decades ago with TCP and IP. This wave has been pushing a fundamental shift in communication.
- The shift is computer-to-computer communication systems replacing people-to-people communication systems.
- Although TCP and IP are computer-to-computer communication software, these programs began an evolution in network hardware that led to computer-to-people software (like web browsers) which in turn opened the door for software (like Priceline, Google, Amazon, Uber) that performed the Search task in the people-to-people transaction system.
- The ability to create a trusted system with networked computers now enables computer-to-people software (like distributed ledgers) to more effectively perform the remaining two tasks, Bargain and Enforce, in the people-to-people transaction system.
3)The industry forces involved in this age of the wave, let’s call it the Bargain and Enforce Age, are more complicated, interconnected and involve more human institutions/bureaucracy than when upgrading the network or commandeering the Search task. An article titled, The Truth about Blockchain in Harvard Business Review touches on this subject.
- This implies the adoption process regarding this new database technology will be difficult.
- During this shift over the past decades, the highway is already littered with thousands of business carcasses. I expect there will be multiples of that number in this bargain and enforce stage of the wave.
- Understanding the competitive industry structure of their targeted transaction system will help entrepreneurs identify strategic risks and business uncertainties and prepare for if, when and how viciously competition may react.
The full article Look Before You Leap